Accumulated Depreciation and Depreciation Expense

This method is particularly useful for assets that are expected to lose value more quickly in their early years of use and then decline at a slower rate over their useful life. For example, it assumes that the asset depreciates at a constant rate over its useful life, which may not always be the case. Additionally, it does not take into account the time value of money, which means that the depreciation expense may not reflect the actual decrease in the value of the asset over time.
Assets that are commonly subject to depreciation include buildings, machinery, equipment, vehicles, and furniture. The adjusting entry for a depreciation expense involves debiting depreciation expense and crediting accumulated depreciation. Accounting PeriodAccounting Period refers to the period in which all financial transactions are recorded and financial statements are prepared.
Explanation of what depreciation is
A provision for depreciation or an accumulated depreciation account is maintained where depreciation is credited separately. The account Accumulated Depreciation is a balance sheet account and therefore its balance is not closed at the end of the year. Accumulated Depreciation is a contra asset account whose credit balance will get larger every year. However, its credit balance cannot exceed the cost of the asset being depreciated. The accounting for depreciation requires an ongoing series of entries to charge a fixed asset to expense, and eventually to derecognize it. These entries are designed to reflect the ongoing usage of fixed assets over time.
How do you write depreciation expense?
- Periodic Depreciation Expense = (Fair Value – Residual Value) / Useful life of Asset.
- Periodic Depreciation Expense = Beginning Value of Asset * Factor / Useful Life.
At the end of the year, Big John would record this depreciation journal entry. It’s a common misconception that depreciation is a form of expensing a capital asset over many years. Depreciation is really the process of devaluing the capital asset over a period of time due to age and use.
Depreciation on Machinery Journal Entry
Useful life – Each asset class has a different useful life. FloQast’s suite of easy-to-use and quick-to-deploy solutions enhance the way accounting teams already work. Learn how a FloQast partnership will further enhance the value you provide to your clients.
- Then a depreciation amount per unit is calculated by dividing the cost of the asset minus its salvage value over the total expected units the asset will produce.
- How to make a journal entry to record depreciation on an asset.
- The accumulated depreciation account is recorded on the balance sheet and shows the total depreciation expense incurred since the asset was acquired.
- By crediting accounts payable, which is aliability account, this entry shows that you owe your vendor $1,000.
Notice that at the end of the useful life of the asset, the carrying value is equal to the residual value. A half-year convention for depreciation is a depreciation schedule that treats all property acquired during the year as being acquired exactly in the middle of the year. Investopedia requires writers to use primary sources to support their work. These include white papers, government data, original reporting, and interviews with industry experts.
Final Thoughts on Expense Tracking and Accounting
An asset’s net book value is its cost less its accumulated depreciation. Assume that ABC company had paid $480,000 for its office building . Say this building has an estimated useful life of 40 years with no salvage value. Using the straight-line method of depreciation, calculate the depreciation expense to be reported on each of the company’s monthly income statements and show the journal entry for this. Depreciation expense is an expense and is therefore treated as an expense account, but unlike most expenses, there is no related cash outflow. When the asset was originally purchased, the company had a net cash outflow in the entire amount of the purchased asset, so over time, there is no further cash-related activity.
- Following are the journal entries of transactions and financial events relating to depreciation.
- Thus, to record the depreciation on the motor vehicle, the correct journal entry would be to debit the depreciation expenses and credit the motor vehicle account.
- Units of production depreciation will change monthly, since it’s based on machine or equipment usage.
- If this allocation is not made, the income statement will reflect a higher income or lower loss.
A) Manufacturing account will be debit because all the expenses relating to production will be debit in this account. When We also invest same depreciation fund money in depreciation fund investment. B) Accumulated depreciation account will be debit because with this, liability will decrease. A)Depreciation on machinery is the loss of business, and every loss will be debited. It doesn’t matter which vendor is displayed since journal entries are not linked to a vendor.
In other words, depreciation is the allocation of the cost of a fixed asset to the period over which the benefit is obtained from the use of the asset. The depreciation entry is an estimate based on the asset’s historical cost, its estimated useful life, and its estimated salvage value. Financial StatementsFinancial statements are written reports prepared by a company’s management to present the company’s financial affairs over a given period . This method requires you to assign all depreciated assets to a specific asset category. An updated table is available in Publication 946, How to Depreciate Property. When using MACRS, you can use either straight-line or double-declining method of depreciation.

Using the direct method, when you realize an accounts receivable account is uncollectible, you write off the amount to bad debt. Here’s how the journal entry for the expense would look. Understand the need to record depreciation for the current period prior to the disposal of property or equipment. After the asset’s useful life is over and when all depreciation is charged, the asset approaches its scrap or residual value.
B) Accumulated depreciation account is just like provision for depreciation account and it will be credit because we are collected all depreciation in the form of accumulated depreciation. It means, we want to maintain our historical cost of machinery at any time except time of sale. A) Profit and loss account complete the double entry record. With this, all expenses and losses account will be closed. So, profit and loss account will be debit in this journal entry. Credits will cause an increase to some accounts such as the revenue, equity, and liability accounts while accounts like the expense and asset accounts will decrease by a credit entry.
In other words, the total amount of depreciation expense recorded in previous periods. Mr. John purchases a piece of machinery for $3,900 and determines its salvage value to be $1,000. If the machinery’s how to record depreciation expense in journal entry useful life is three years, what will be the depreciation expense if Mr. John is recording depreciation monthly? Assume a company, ABC Ltd, has a property, plant & equipment account.
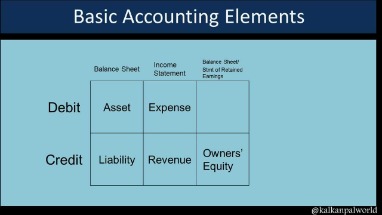
Is depreciation debit or credit in journal entry?
A normal depreciation account is a debit in nature since it is an expenditure, while accumulated depreciation is of credit in nature as it is initially recorded when the depreciation account is recorded as an expense.
